äâ¹â€ã©â€ºâ¢ æâ⧠çâ¢â¾ èââ äâºå¾ã§â€˜å¸ã§å½â€¹ èâµâ¤ èå¾â Fan Art
When files are moved betwixt different operating systems, or stored in a mutual file system such equally AFS, you may sometimes find that characters such every bit ÅÄÖ are shown incorrectly.
A grapheme encoding determines which binary sequence is used to represent each letter of the alphabet, or other character. Many different means to encode text take been used throughout the years. CSC's Unix systems have traditionally used "Latin-i" (ISO-8859-i), which contains the messages used in western European languages. Other operating systems have used other encodings, e.g. "Mac Roman" on Mac Os, "CP-1252" on MS Windows, or "CP-437" on MS DOS. All of these are extensions of ASCII (basically, American messages, digits and punctuation), which ways that such characters are displayed correctly. But accented letters differ. In item, the Swedish letters ÅÄÖ are not displayed correctly
These days, most OSs can use some form of UTF-viii, but you may demand to configure the applications to use it. To practise so you choose a locale, which defines formatting many settings specific to a language and region, for example:
- Number formatting (e.g. using "1 234,5" or "one,234.5")
- Appointment and time formatting
- String collation (i.eastward. sort social club, so that "ångström" is sorted nether A in English but Å in Swedish)
The locale is written every bit «language»_«variant».«encoding», due east.g. "en_US.UTF-eight" (American English, UTF-8) or "en_GB.ISO8859-1" (British English language, latin-ane).
Wikipedia'south caption of latin1 (external link)
Wikipedia's explanation of locales (external link)
Converting a file
To convert the contents of a file, you can open it in a locale-enlightened editor, and "save as..."
a different encoding, or use the iconv command-line tool:
iconv -f iso8859-1 -t utf-8 < original.txt > new.txt
When logging in remotely (with SSH), you can normally configure your local settings to be forwarded. Unfortunately, non all SSH servers support this. Currently (as of November 2010), CSC's Solaris SSH server does not permit forwarding of environment variables, which is needed for this to work. The relevant locales (en_US.UTF-eight, sv_SE.UTF-eight) are bachelor on Solaris, and you tin set them manually, simply they won't exist used by default.
Problem: ÅÄÖ shown as ���
Your awarding uses latin1 characters, but your terminal (or editor) tries to brandish them as UTF-8. Configure your application to utilise UTF-8 (see below), or alter your terminal settings to utilise ISO-8859-1.
Problem: ÅÄÖ shown equally åäö
Your application uses UTF-eight, but they are displayed as latin1. Configure your awarding to use ISO-8859-1 (run across below), or change your concluding settings to utilise UTF-8.
Problem: ÅÄÖ shown as ���
Your awarding is printing U+FFFD, the Unicode replacement graphic symbol (�, usually displayed as a question marker on inverted background). This is then converted every bit if it were in latin1 to UTF-8 (a U+FFFD grapheme in UTF-8 uses three bytes). Check the settings for all applications — including the terminal window — to ensure that they all agree on which encoding to use.
Select locale (application settings)
If your application is locale aware (most are, but not some legacy CSC applications), then you tin can select the locale by
consign LC_ALL=en_US.UTF-viii ## bash
setenv LC_ALL en_US.UTF-viii ## tcsh
and and then run your application. To only configure the grapheme encoding, change the LC_CTYPE environment variable instead.
You tin also select which locale to apply when you log in locally, but this may crusade trouble when yous use a dissimilar operating system. We recommend that you lot use the default settings and re-configure the applications instead.
Configuring terminal encoding
Ubuntu
The encoding used past Gnome'south last can be change under Terminal and then Set Character Encoding, merely unless you have previously washed and so, you need to add the "Western (ISO-8859-1)" encoding.
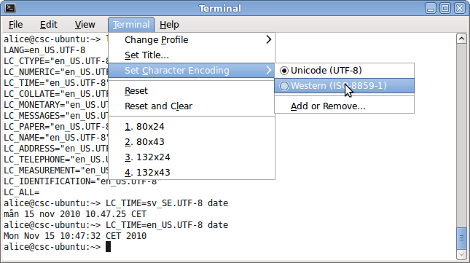
Mac OS Ten
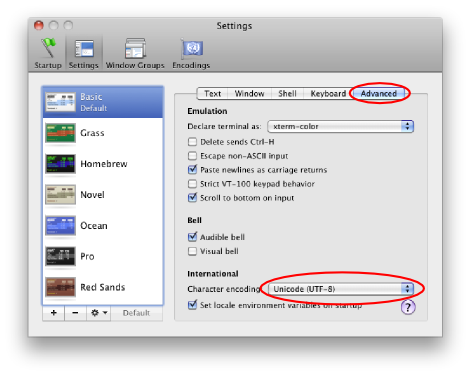
The default settings for Terminal.app is to employ UTF-eight. This can exist changed past going to Terminal then Preferences… then Advanced.
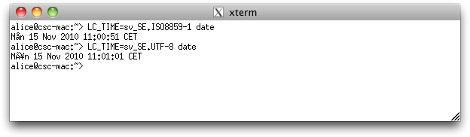
The default for X11.app's xterm is to use latin1. You tin can change this by editing the startup sequence for X11, but it's easier to just use Terminal.app.
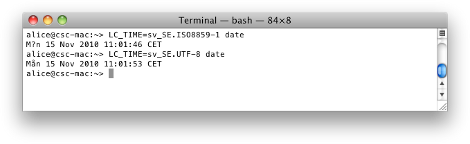
MS Windows
PuTTY's settings can be changed nether Window and then Translation in the configuration dialog.
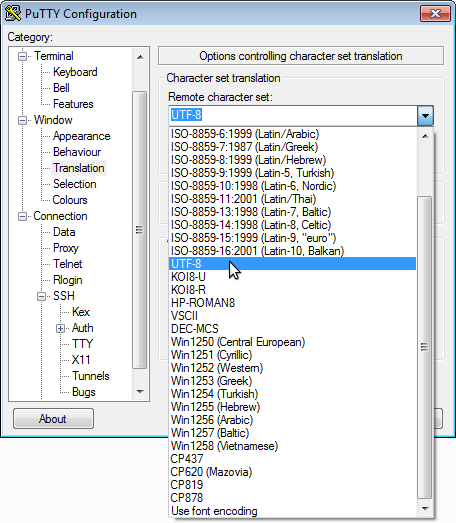
CSC's Windows computers currently run SSH Secure Shell from Tectia (formerly SSH Communications Security Corp). It is not UTF-8 aware, and will default to using latin1 encoding.
Source: https://intra.kth.se/en/it/arbeta-pa-distans/unix/encoding-1.71788
0 Response to "äâ¹â€ã©â€ºâ¢ æâ⧠çâ¢â¾ èââ äâºå¾ã§â€˜å¸ã§å½â€¹ èâµâ¤ èå¾â Fan Art"
Post a Comment